Total Contract Value (TCV) is the sum of a contract's Total Contract Line Values (TCLV). The Total Contract Line Value (TCLV) of a line is its Sales Price * Number of Terms.
Several factors affect TCV and TCLV calculations:
- A contract without an End Date (a continuous contract) does not have a TCV calculated, but its lines may have their TCLVs calculated.
- Discounts, pricing structures, and quantity breaks are applied to the Sales Price before TCLV is calculated.
- Any contract lines where the Billing Type is "One-off" have their TCLV set to the Sales Price.
- Contract lines that are not "One-off" lines do not have their TCLV calculated if any of the following conditions apply:
- The line does not have an End Date
- The line does not have a Sales Price
- The line does not have a Billing Term
- When a proration policy is assigned to a contract, any "Recurring Fixed" contract lines are billed a prorated value if their start or end periods are partial periods.
- "Recurring Variable" lines are billed based on customer usage so their TCLV is not calculated unless a quantity is supplied as an estimate of usage. If a quantity is supplied, TCLV is calculated in the same way as for "Recurring Fixed" lines.
Example
A contract starts on August 1, 2017 and ends on August 31, 2017. It has three lines as shown in the table below.
|
Billing Type |
Sales Price |
Start Date |
End Date |
Billing Term |
TCLV without proration |
TCLV with Actual Days in Billing Period proration |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| One-off | 100 | Aug 1, 2017 | Aug 31, 2017 | 100 | 100 | |
| Recurring Variable | - | Aug 1, 2017 | Aug 31, 2017 | - | - | |
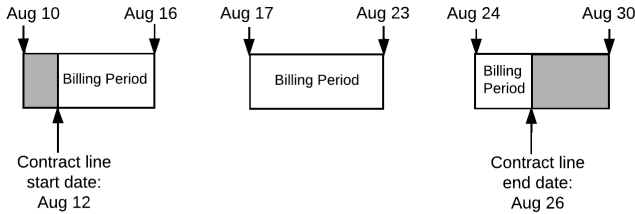
| Recurring Fixed | 70 | Aug 12, 2017 | Aug 26, 2017 | WB + 3d | 210 | 150 |
| TCV | 310 | 250 |
The TCLV for the "One-off" contract line is its sales price (100) regardless of whether or not proration applies to the contract.
There is no TCLV for the "Recurring Variable" contract line because it will be billed on usage and no quantity has been supplied as an estimate of usage therefore Sales Price cannot be calculated.
The TCLV of the "Recurring Fixed" line varies if proration applies to the contract. Without proration, the TCLV is 210 because the line extends across three billing periods (70 * 3 = 210). With proration, the TCLV is the sum of:
charge for partial start period + charge for one whole period + charge for partial end period
As shown in the table above, if the contract's proration policy uses the Actual Days in Billing Period calculation method and the week begins on Monday, the TCLV will be 50 + 70 + 30 = 150 because the partial start period is 5 days, the second period is a whole period of 7 days, and the partial end period is 3 days.
Different proration calculation methods will result in different values for the start and end periods. See Proration Policies and Calculating Partial Periods for more information.